Oxford remains a vibrant Transgender community in Historic England. Although Oxford is a university with a rich history of medieval warfare and religious affiliations, this city in southern England is also known for its diverse...
UK TS Dating
Best Locations for Hot Bristol Trans Dating Meet Ups
Bristol is one of the UK’s largest cities and consequently has a diverse cultural scene and is seen as a transgender friendly place for trans people to hook up and date. There are a number of pubs and clubs that are...
Top Cardiff TS Dating Bars and Clubs for Transgender
Step into the heart of Wales’ capital, where the night comes alive with a kaleidoscope of inclusive spaces that celebrate diversity in all its forms. Cardiff has earned its stripes as a beacon of acceptance, where the...
Latest Manchester Trans Dating Contacts
Manchester, often referred to as the “Rainbow Capital of the North,” is a vibrant and inclusive city that has a longstanding history of supporting and celebrating the trans community and offers a plethora of TS Dating...
The Top Ten Transgender-Friendly Cities in the UK
The United Kingdom stands out for its progressive stance on LGBTQ+ rights and inclusion, with numerous cities championing diversity and acceptance. From vibrant pride parades to pioneering legal protections, the UK offers a...
Great Guide to Edinburgh’s Top Transgender Clubs and Bars
Edinburgh, the capital city of Scotland, is known for its rich history, stunning architecture, and a vibrant cultural scene. It’s also a city that proudly embraces diversity, making it an inclusive and welcoming home for...
The Way Out Transgender Club London
The WayOut Club, nestled at The White Swan on Commercial Road in London, is more than just a venue; it’s a vibrant celebration of diversity and identity. Marking its 30th anniversary in 2023, this leading transgender...
Sensational Transgender Webcams
Introducing the epitome of grace and allure – our stunning transgender webcam models whose beauty and sexuality transcend boundaries. Delighting in the art of seduction, they invite you into a world where confidence meets...
Best TS Dating Leeds Hook Ups
Leeds, a vibrant city in West Yorkshire, is renowned for its inclusivity and welcoming atmosphere, making it a thriving hub for the LGBTQ+ community. The city boasts a rich transgender dating nightlife scene with an array of...
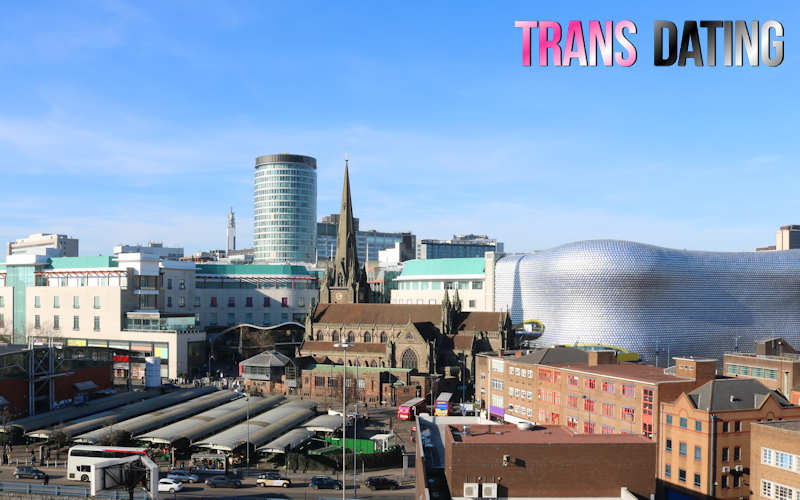
Best TS Dating Birmingham Locations
Birmingham, the heart of the West Midlands, is a vibrant and diverse city known for its rich cultural heritage and inclusive atmosphere. The TS Dating community in Birmingham has flourished over the years, making it home to a...